Dividing a scalar by a vector
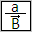 |
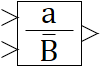 |
| Vector | C | ST | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block implements the division of the first scalar input value into each of the elements of the second input vector signal:
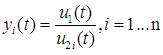
where u1(t) is the signal at the first input, scalar one; u2 i(t) is the i-th element of the input vector signal at the second input u2(t); yi(t) is the element of the output vector signal, y(t), n is the dimension of the second input signal and the output signal of the block. The dimension of the output is equal to the dimension of the first input.
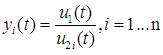
where u1(t) is the signal at the first input, scalar one; u2 i(t) is the i-th element of the input vector signal at the second input u2(t); yi(t) is the element of the output vector signal, y(t), n is the dimension of the second input signal and the output signal of the block. The dimension of the output is equal to the dimension of the first input.
Mandatory сondition: u2 i(t)≠0.
Inputs
- number - port for the input scalar (dividend);
- vector - a port for the input vector (divisor).
Outputs
- output - port of the resulting vector.
Properties
- Maximum value at division of number by 0 - the value of block output at division by 0;
- Warn when dividing by 0 - whether or not to issue a message that division by 0 has occurred in the block.
Parameters
none
Note:
The dimension of the output signal is equal to the dimension of the second input signal. If the second input signal is scalar, the block realizes the division of the first input signal by the second input signal, in which case the output is a scalar value.