Matrix packing
 |
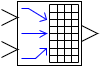 |
| Vector | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block implements the conversion of several input vector signals into one vector output signal according to the following algorithm:
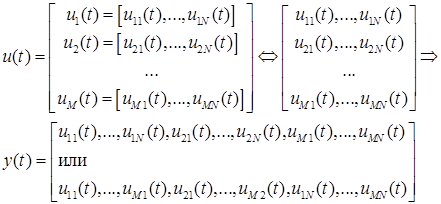
or
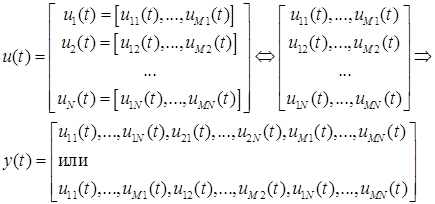
where y(t) is the vector output signal, ui(t) is the vector input signals. The input vectors ui(t) interpreted as rows or columns of the [N×M] size matrix are transformed into a single vector output y(t) (depending on the packing option: by rows or by columns).
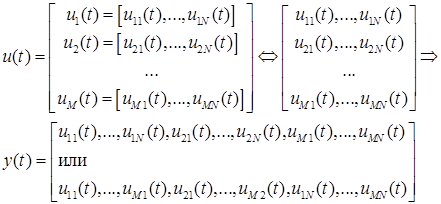
or
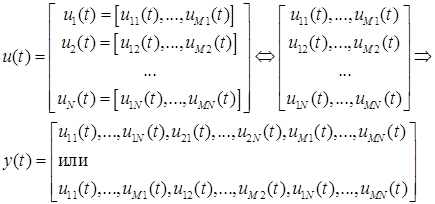
where y(t) is the vector output signal, ui(t) is the vector input signals. The input vectors ui(t) interpreted as rows or columns of the [N×M] size matrix are transformed into a single vector output y(t) (depending on the packing option: by rows or by columns).
Inputs
- inport_n - port for input rows/columns of the formed matrix. The number of input ports depends on the number of rows/columns in the block properties.
Outputs
- OUTPORT - port for outputting the formed matrix.
Properties
- Number of rows in the matrix – M.
- Number of columns in the matrix – N.
- Matrix is unpacked via – the option of "unpacking" the matrix of input signals (by rows or by columns).
- Pack the matrix via – the option of "packing" the output signal (by rows or by columns).
Parameters
none
Note:
- By default, the block packs two "two-wire" input signals into a matrix of size [2×2]. In this case, the input signals are perceived as rows of the matrix and the matrix is packed in rows.
- Named properties can be set as local model variables (submodels) in a programming language script, as global project signals using the Tools → Signals main menu item, or as external project signals using an attachable signal database.