Multiplication of a matrix by a vector
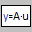 |
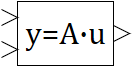 |
| Vector | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block implements the procedure of multiplying a square matrix by a vector of the corresponding dimension:
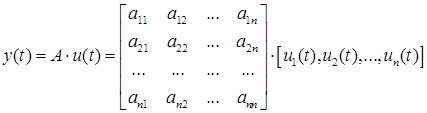
where A is the matrix of coefficients; x(t) is the solution vector; u(t) is the vector of the right-hand parts, y(t) is the vector at the output of the block.
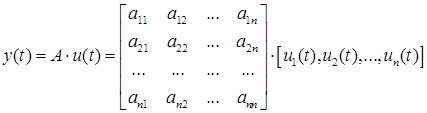
where A is the matrix of coefficients; x(t) is the solution vector; u(t) is the vector of the right-hand parts, y(t) is the vector at the output of the block.
Inputs
- matrix - the a port for entering the matrix A, represented as a vector of coefficients when unpacking the matrix by rows. The dimension of the vector signal on the 1st input port should be equal to n×n, where n is the dimension of the matrix;
- vector - the port for entering the vector u(t). The dimension of the vector is n.
Outputs
- output - the port for vector y(t) output. The dimension of the vector is n.
Properties
none
Parameters
none
Example
It is required to multiply matrix A by vector u if:
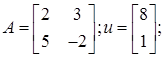
the result of multiplication is obvious: a column vector, the elements of which are 19 and 38. The figure below shows a structural diagram for solving this problem. Typical Multiplier blocks are used to generate input vector signals:
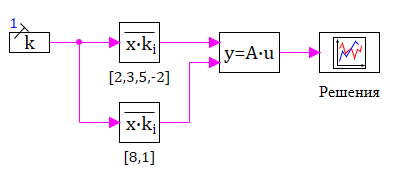
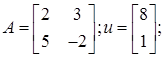
the result of multiplication is obvious: a column vector, the elements of which are 19 and 38. The figure below shows a structural diagram for solving this problem. Typical Multiplier blocks are used to generate input vector signals:

Note:
the block performs multiplying the square matrix by the vector after each successful integration step.