Mass
 |
 |
| C | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block is designed to simulate the translatory motion of a body having a constant mass. The block calculates the linear acceleration of the body and determines the speed and position of the body using integration. Linear acceleration a in m/s2 is calculated by the formula:
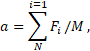
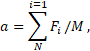
where:
- N – number of blocks connected to this block by a branching mechanical communication line
- Fi – force coming from the i-th block, N
- M – body mass, kg
The value of body mass M in kg is displayed next to the block.
Inputs
Outputs
| Name | Description | Connection line type |
|---|---|---|
| R | Port for connecting model blocks to a moving body (rod) | Translatory mechanics |
Properties
| Name | Parameter | Description | By default | Data type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass, kg | M | Body mass | 1 | Вещественное |
| Initial position, m | S0 | Body initial position | 0 | Вещественное |
| Initial speed, m/s | V0 | Body initial speed | 0 | Вещественное |
Parameters
| Name | Parameter | Description | Data type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position, m | S | Position of the body | Вещественное |
| Speed,m/s | V | Body speed | Вещественное |
| Acceleration, m/s2 | A | Body acceleration | Вещественное |
| Force, N | F | Total force applied to the body | Вещественное |
| Power, W | Q | Mechanical power of the total force | Вещественное |
Examples
Examples of block application: