Circular integrator
 |
 |
| Vector | C | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block is vectorized. It implements the mathematical model of the link, the dynamics of which is described by a linear ordinary differential equation (ODE) of the following form:
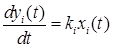
where xi(t) is the i-th element of the block input signal, ki is the element of the gain vector, yi(t) is the element of the output signal from the block. Moreover, the output function yi(t) takes a value in the range from 0 to 2Pi, describing the changing of the output value along a closed circle. Under zero initial conditions, the dynamics of the block can be represented by the following transfer function:
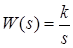
therefore, there is an image of the transfer function of the ideal integrating link in the block icon.
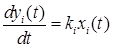
where xi(t) is the i-th element of the block input signal, ki is the element of the gain vector, yi(t) is the element of the output signal from the block. Moreover, the output function yi(t) takes a value in the range from 0 to 2Pi, describing the changing of the output value along a closed circle. Under zero initial conditions, the dynamics of the block can be represented by the following transfer function:
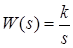
therefore, there is an image of the transfer function of the ideal integrating link in the block icon.
Inputs
- input - input signal.
Outputs
- output - output converted signal.
Properties
- Gain coefficients – vector of coefficients ki, by which the input value is multiplied;
- Initial conditions – vector of initial values yi of the block output.
Parameters
- Dynamic variables - internal block condition variables;
- Derivatives - internal block condition variables.
Note:
by default the block implements integration of scalar input signal.