General transfer function
 |
 |
| Vector | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block implements the mathematical model of the link, the dynamics of which (for each scalar signal) is described by a linear ordinary differential equation (ODE) of the following form:
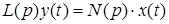
where
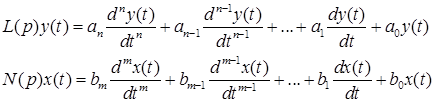
ai, bj - coefficients (i=0...n, j=0...m, n≥m); x(t) - input signal to the block (can be vector, then the vectors of coefficients and the block output will also be vector of the same dimension), y(t) - output signal from the block. Under zero initial conditions, the dynamics of the block can be represented by the following transfer function:
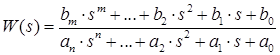
The dimensions of the input signal, output signal and coefficient vectors must match.
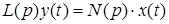
where
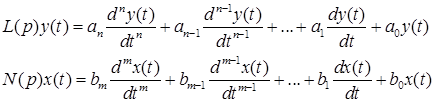
ai, bj - coefficients (i=0...n, j=0...m, n≥m); x(t) - input signal to the block (can be vector, then the vectors of coefficients and the block output will also be vector of the same dimension), y(t) - output signal from the block. Under zero initial conditions, the dynamics of the block can be represented by the following transfer function:
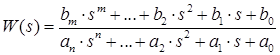
The dimensions of the input signal, output signal and coefficient vectors must match.
Inputs
- input - input signal.
Outputs
- output - output converted signal.
Properties
- Numerator coefficients – vector bj, with dimension [m]. The vector should be written starting from the zero element ( [b0, b1,b2...bm] ).
- Denominator coefficients – vector ai, dimension [n]. The vector must be written starting from the zero element ( [a0, a1, a2...am] ).
- Initial conditions – vector of initial values yi of the block output.
Parameters
- Dynamic variables - internal block condition variables;
- Derivatives - internal block condition variables.
Note:
By default, the block implements scalar input signal processing.