Nonlinear rotary spring
 |
 |
| C | |
| in the palette | on the schematic |
The block is designed to simulate a nonlinear rotary spring with a constant spring constant.
The deformation of the spring φ in rad is determined by the formula:
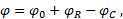
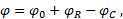
where:
- φ0 – initial spring extension, rad
- φC and φR – turn angles at the ports "C" and "R", respectively, rad
The dependence of the torque on the turn angle can be defined using a polynomial or a table.
Symmetric polynomial
This method allows you to define the dependence of the torque on the turn angle by a polynomial which is symmetric relative to zero:
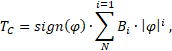
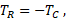
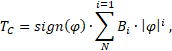
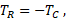
where:
- TC and TR – torques applied to ports "C" and "R", respectively, Nm
- Bi – i-th element of the vector of spring constants, N·m/rad
- N – number of elements in the vector of spring constants
Asymmetric polynomial
This method allows you to define the dependence of the torque on the turn angle separately for extension and compression. The polynomial Bp defines the dependence at a positive deformation value (extension) and the polynomial Bn defines the dependence at a negative deformation value (compression):
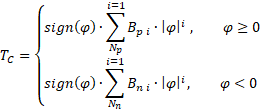
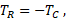
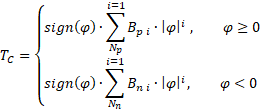
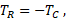
where:
- TC and TR – torques applied to ports "C" and "R", respectively, Nm
- Bpi – i-th element of the vector of spring constants Bp, N·m/rad
- Bni – i-th element of the vector of spring constants Bn, N·m/rad
- Np – number of elements in the vector of spring constants Bp
- Nn – number of elements in the vector of constants Bn
Table
This method makes it possible to calculate the spring torque depending on the turn angle by interpolating a given table. If the deformation value exceeds the specified vector of the deformation values, extrapolation is not carried out.
Inputs
| Name | Description | Connection line type |
|---|---|---|
| C | Port for connecting a conditionally fixed case (case) | Rotary mechanics |
| R | Port for connecting a conditionally moving shaft (rotor) | Rotary mechanics |
Outputs
None.
Properties
| Name | Parameter | Description | By default | Data type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameterization type | par_type | Allows you to specify the type of dependence of the torque on the turn angle. The possible values are: "Polynomial", "Table" | Polynomial | Перечисление |
| Symmetry | sym_type | Allows you to define a polynomial that is symmetric with respect to zero. The property is available when you select the "Polynomial" parameterization type. The possible values are: "Yes", "No" | Yes | Двоичное |
| Vector of spring constants, Nm/rad | B | Vector of spring constants. The property is available when the "Polynomial" parameterization type is selected and the "Symmetry" property is enabled | [0 , 1 , 0 , 0.1 , 0 , 0.01] | Массив |
| Vector of spring constants for Fi ≥ 0, Nm/rad | Bp | Vector of spring constants at positive deformation (extension). The property is available when the "Polynomial" parameterization type is selected and the "Symmetry" property is disabled | [0 , 1 , 0 , 0.1 , 0 , 0.01] | Массив |
| Vector of spring constants for Fi < 0, Nm/rad | Bn | Vector of spring constants at negative deformation (compression). The property is available when the "Polynomial" parameterization type is selected and the "Symmetry" property is disabled | [0 , 10 , -0.1 , 1] | Массив |
| Vector of deformation values, rad | Fx | Vector of deformation values. The property is available when you select the "Polynomial" parameterization type. | [-1 , -0.5 , -0.3 , -0.1 , 0.1 , 0.3 , 0.5 , 1] | Массив |
| Vector of spring torques, Nm | Ty | Vector of spring torques. The property is available when you select the "Polynomial" parameterization type. | [-10 , -4 , -2 , -0.5 , 0.5 , 2 , 4 , 10] | Массив |
| Initial extension (Fir - Fic), rad | Fi0 | Initial spring extension at zero angles of rotation at the block ports. A negative value sets the pre-compression | 0 | Вещественное |
Parameters
| Name | Parameter | Description | Data type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring deformation, rad | Fi | Spring extension. Negative values mean compression | Вещественное |
| Elastic torque, Nm | T | Torque transmitted to port "R" | Вещественное |
Examples
Examples of block application: